Key Takeaways
- Offset vs digital printing is about printing methods, of course, but these days it’s mostly about cost and the size of the project.
- For large print quantities, particularly those with many pages, offset printing will be a good choice. It’s cheaper and faster (for the printing company). We can print offset at 240,000 sheets per hour for standard 2-sided paper, while our fastest digital printer is about 7,200 pages per hour!
- For smaller quantities (generally under 1,000 catalogs, for example), digital printing will make more sense. For large print runs, like sales flyers for a grocery store, offset printing will be superior.
- Confused? The good news is we help you make these decisions on every marketing print job, providing the best outcome for your budget and needs.
When it comes to choosing a printing process, most of our clients don’t actually have a strong opinion: they just want great-looking marketing materials!
BUT, understanding the strengths of offset printing vs digital printing can be helpful.
At our print shop, we’ve mastered both methods and have cutting-edge equipment on both “sides of the aisle” to tailor our capabilities to each client or project. Whether you need personalized sales postcards or thousands of catalogs, we’ve got you covered. Let’s dig into what makes each of these printing methods shine.
What Is Offset Printing?
Offset printing is the old-school champ of the printing world, known for using a metal plate to transfer ink to a rubber sheet and then onto the printing surface. This method is perfect for large print runs thanks to its incredible efficiency and ability to create high-quality prints.
For projects like catalogs, newsletters, sales mailers, or presentation folders, offset printing is a smart choice. While it involves upfront costs for plates and setup, the per-piece cost drops significantly with higher quantities. Offset printing also works wonders with traditional offset stocks, producing crisp, smooth results, especially when gradients or large solid colors are involved. And let’s not forget, laminated finishes stick better to offset prints, making it a go-to for book covers, menus, and other durable items.
What Is Digital Printing?
Digital printing skips the plates entirely, sending your design straight from a print file to the paper.
It’s a fast, flexible option that’s best for smaller print jobs or projects requiring variable data printing. Think personalized data like names, mailing addresses, or custom designs for each piece—digital printing handles these easily.
The technology behind digital printing includes advanced inkjet technology and toner-based digital presses. These processes excel at providing exact amounts of ink, reducing waste, and offering eco-friendly options like biodegradable inks and recyclable paper stocks.
And while digital printing used to be slower, today’s machines are faster than ever, making them ideal for tight deadlines and last-minute projects. Additionally, digital printing is considered more sustainable printing due to its use of biodegradable inks and elimination of harmful chemical washes.
| What Kinds of Printers Do We Use At Little Mountain Printing? Our largest offset printer is called a Heidelberg, and it is over 60 feet in length! We also have Ryobi Mitsubishi Graphic Technologies, Shinohara, and Toko offset printers. We use Konica Minolta and Rapid Color Press digital printers. |
|---|
Key Differences Between Offset and Digital Printing
So, what’s the real difference between offset printing and digital printing methods? While those of us in the printing industry might have strong feelings about both, and things are changing quickly as technology evolves, there are some basic differences that are easy to understand.
- Offset printing works best with high quantities and high-quality prints, especially when the design includes gradients, solid colors, or full color printing. While digital inkjet printing has closed the gap in quality over the years, offset still delivers smoother, crisper results for certain applications.
- Cost-wise, digital printing is your go-to for low-volume jobs. Offset printing, on the other hand, becomes more economical as the quantity increases.
- Offset also supports a broader range of paper stocks, including glossy finishes and offset stocks with dull silk. Digital printing offers unmatched convenience for quick, small-scale jobs and projects that require variable data, with no need to wash plates and no risk of wet ink.
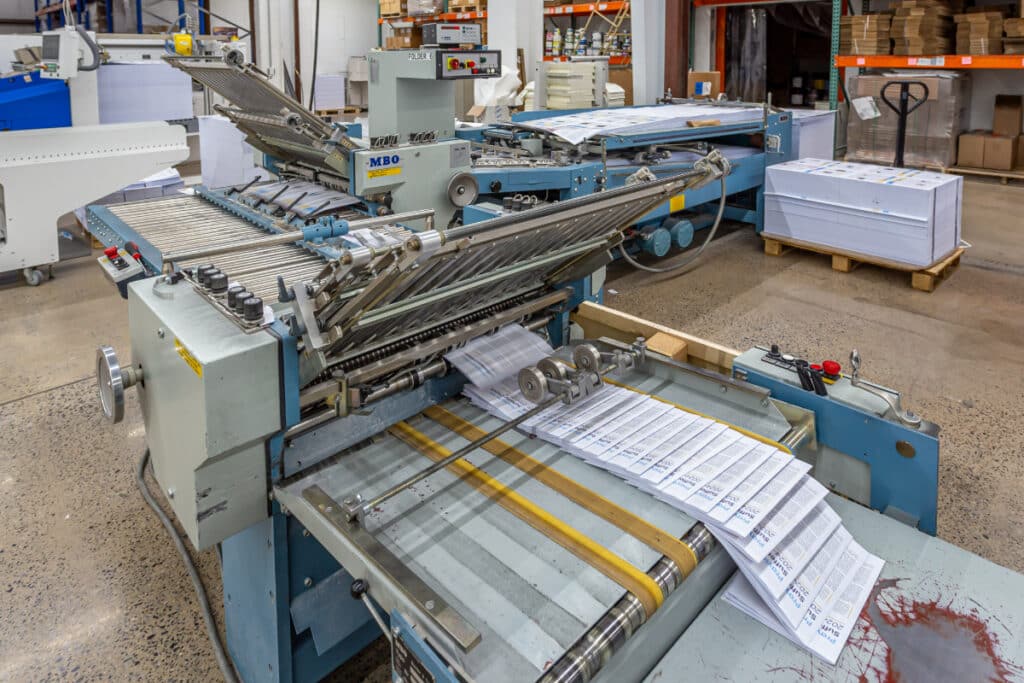

Offset Printing Downsides
Offset printing, while reliable and perfect for high quantities, does come with a few disadvantages.
The most notable downside is the initial setup cost, which includes preparing plates and calibrating the printing presses. This makes offset printing cost-effective for small print runs of one plate. Additionally, the process can take longer to get started, as it requires more preparation compared to digital printing. Furthermore, offset printing uses oil-based inks that may require special handling and additional drying time. Advancements like UV drying (we do this!) have mitigated some of these challenges.
Digital Printing Downsides
Digital printing, while versatile, has its limitations.
One significant downside is that the cost per piece remains relatively stable regardless of the print run size, making it less economical for large quantities. Additionally, digital presses have a shorter lifespan and may require regular maintenance, including replacing parts like corona wires. Print quality, while excellent for most applications, might show banding or roller marks, particularly on larger solid color areas. Digital printing also tends to have a more limited range of paper stocks and finishes compared to offset printing. For example, traditional offset stocks with dull silk and glossy or specialty laminations often adhere better with offset printing methods.

Other Factors
Hybrid Printing: Combining Offset and Digital
Hybrid industrial printing systems combine the best of both worlds, integrating offset printing with inkjet technology.
This innovative approach streamlines the production process, enabling a single-pass line optimized for offset printing while incorporating the flexibility of inkjet technology. Hybrid printing is ideal for projects requiring both the high-quality output of offset and the customization capabilities of digital.
Printing Medium and Substrate Options
The choice of materials matters, too, and both offset and digital printing offer distinct advantages.
Digital printing supports a variety of media, such as fabric, folding cartons, plastics, heavyweight papers, synthetic substrates, and thick cardstock. However, it is limited in handling larger or unusually shaped print sizes.
Offset printing also tends to crack less on paper folds. Heat & hard toner with digital printing make can paper fibers crack more easily when the paper is folded. If the piece is difficult to score or crease prior to folding, we generally prefer offset printing. For the outsides of catalog & book covers, for example, we usually prefer offset printing over digital to avoid fiber cracking–if the quantity allows for it.
Ultimately, offset printing provides greater flexibility in terms of paper stocks, sizes, and folds, making it the preferred choice for projects requiring more traditional offset stocks or larger dimensions.
Customization and Personalization Options
Customization and personalization options are becoming increasingly important in the printing industry, especially for targeted marketing campaigns.
Digital printing offers variable data printing, which enables individualization of texts and images from impression to impression. This is good for businesses that need to personalize their prints, such as direct mail campaigns, event tickets, and personalized marketing materials.
Offset printing, on the other hand, is not suitable for variable data printing. The traditional offset printing process involves creating static plates, which means every print in a run will be identical.
Equipment Costs and Investment
Printing equipment varies significantly in cost and complexity.
Thermal inkjet (TIJ) offers the lowest cost of entry and ownership, making it a popular choice for smaller operations. Piezo drop-on-demand technology is a step up, offering enhanced quality at a moderate investment. Finally, continuous inkjet (CIJ) systems demand more operator training, higher maintenance, and significant downtime, making them better suited for high-volume, industrial use…. much like offset printing!
Which Printing Method Is Right for Your Project?
The choice between offset and digital printing depends on your needs, really.
If you’re planning a 50,000-piece catalog run, offset printing is the clear winner.
But if you’re printing 500 custom postcards with personalized mailing addresses, digital printing is the way to go. Budget, project size, and desired finish all play a role in deciding which method fits best.
The good news? We do both, AND we help our clients make sense of what, how, and why we’re recommending either approach to printing awesome marketing materials.

Why Choose LMP for Your Printing Needs? Experience, Plus The Benefits of Both Offset and Digital Printing!
We are delighted to offer you both offset and digital printing services. We can handle everything from large-scale print runs to small, personalized projects.
As a Lancaster County print shop with state-of-the-art equipment, hands-on customer service, and a commitment to delivering high-quality prints every time, we’re here to help your project stand out. Whether it’s catalogs, postcards, newsletters, or custom designs, our team is ready to bring your ideas to life.